|
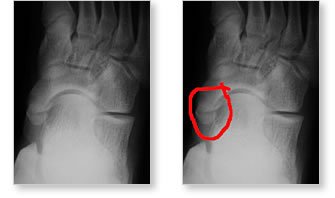
The pictures above are XR's of the foot in an adolescent with an accessory navicular. The extra bone is circled in red in the XR on the right. |
Accessory Navicular Syndrome
Anatomy & Synopsis
In
the child, the bones of the foot occasionally develop abnormally and an extra
bone called an accessory navicular is present towards the inside of the foot, in
front of the ankle. This bone is present in approximately 10% of the general
population but not large enough to cause symptoms in the majority of these
individuals.
|
|
||
|
||
The extra bone
lump present in childhood can be quite uncomfortable because it rubs on shoes.
In addition, the feet associated with the accessory navicular are invariably
flat. The flat-footedness associated with the accessory navicular usually brings
the child for treatment.
If the child is active and involved in various athletic activities, this will
aggravate the inflammation of the tendon that attaches to the accessory
navicular. This tendon is called the posterior tibial tendon and is responsible
for maintaining the strength of the arch of the foot.
Treatment
Treatment of
the accessory navicular begins with rest. Rest may include activity modification
or temporary immobilization in a boot or a brace.
Once the inflammation subsides the foot needs to be supported. The support
consists of a specially designed orthotic arch support. Occasionally, the
orthotic will often dig into the edge of the accessory navicular bone under the
arch of the foot. This is very uncomfortable. For this reason the orthotic
support needs to be carefully made. The orthotic support will help control (but
not cure) the flat foot and will often decrease the inflammation on the
navicular.
Once the navicular inflammation has lessened it is not necessary to perform
surgery unless the foot becomes progressively flatter or continues to be
painful. For these children, surgery can completely correct the problem by
removing the accessory navicular bone and tightening up the posterior tibial
tendon that attaches to the navicular bone. The strength of this tendon is
integral to the success of this surgery as well as the arch of the foot.
Following surgery the child is able to begin walking on the foot (in a cast) at
approximately two weeks. The cast is worn for an additional four weeks. A small
soft ankle support brace is then put into the shoe and worn with activities and
exercise for a further two months.