Plantar Fibromatosis
Synopsis
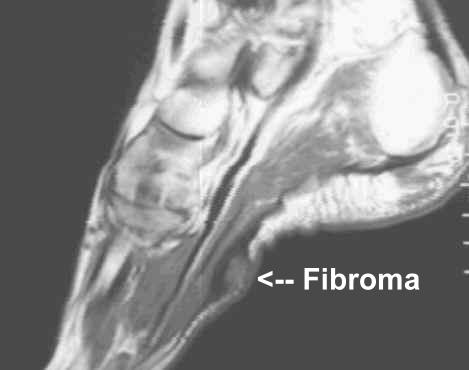
Within the arch of the foot, firm, nodular masses may form. These can occur as a single mass or in clusters. They are called plantar fibromas and are a non-cancerous tumor that forms within a ligament in the arch of the foot called the plantar fascia. Frequently, they will slowly enlarge causing pain while walking. Their cause cannot always be determined. Damage to the tendon will cause their occurrence and there is an association with taking the drug Dilantin. In 10% of the cases, patients will also demonstrate similar lumps in the palms of the hands called Dupuytren’s Contracture.

Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam. Biopsy of the masses is not recommended. The act of biopsy may cause the fibroma to enlarge. When the mass is removed a definitive diagnosis is provided by examination by microscopic examination by a pathologist
Treatment consists of padding the area to reduce pressure. Functional foot orthotics will take the strain off of the plantar fascia ligament and sometimes cause the fibromas to shrink in size. Cortisone injections are of little value and may even stimulate the mass to enlarge or spread. Surgical excision of the mass requires removal of most of the plantar fascia. Simple excision of the mass without removal of the entire ligament generally results in recurrence of the mass. Whenever surgery is contemplated, the patient should wear a functional foot orthotic following the surgery. The orthotic helps to accommodate for the loss of the plantar fascia and its effect on foot function.